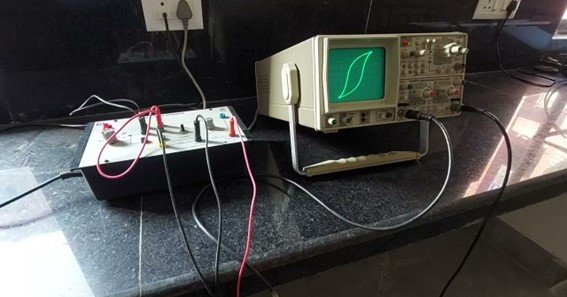
Magnetic hysteresis is a crucial phenomenon in materials science, particularly in the behavior of ferromagnetic materials like iron. It refers to the lag between changes in an external magnetic field and the corresponding changes in the material’s magnetization. This lag creates a hysteresis loop, which is essential for understanding and designing various magnetic and electrical devices.
The Mechanics of Magnetic Hysteresis
Magnetic hysteresis occurs because the magnetic domains within a material, which are small regions with aligned magnetic moments, do not immediately reorient themselves when the external magnetic field changes. As a result, the material retains some magnetization even after the external field is removed, a property known as remanence or residual magnetism. The process of magnetizing and then demagnetizing a material generates a hysteresis loop, which graphically represents the relationship between the magnetic field (H) and the magnetic flux density (B)
Importance of the Hysteresis Loop
The hysteresis loop provides valuable insights into a material’s magnetic properties, such as its coercivity—the resistance to becoming demagnetized—and retentivity, the ability to retain magnetization. The area within the hysteresis loop represents hysteresis loss, which is energy lost as heat during the magnetization cycle. Understanding these properties is crucial in designing materials for specific applications.
Applications of Magnetic Hysteresis
- Data Storage: Magnetic hysteresis is fundamental in data storage technologies like hard drives and magnetic tapes. These devices rely on the ability of materials to retain magnetic states, representing binary data (0s and 1s)
- Transformers and Motors: In electrical engineering, materials with low hysteresis loss are used in transformers and motors to minimize energy loss and improve efficiency.
- Magnetic Sensors: Hysteresis is also critical in the functioning of magnetic sensors, which detect changes in magnetic fields for applications ranging from navigation systems to industrial machinery.
- Magnetic Shielding: Materials with specific hysteresis properties are used in magnetic shielding to protect sensitive electronic devices from external magnetic fields.

FAQ
- What is magnetic hysteresis?
Magnetic hysteresis refers to the lag between the change in an external magnetic field and the change in magnetization of a material, creating a hysteresis loop. - Why is the hysteresis loop important?
The hysteresis loop helps in understanding key magnetic properties like coercivity, remanence, and energy loss in materials, which are crucial for various applications. - What is hysteresis loss?
Hysteresis loss is the energy dissipated as heat during the magnetization and demagnetization cycle of a material, which is represented by the area within the hysteresis loop. - How is magnetic hysteresis used in data storage?
Magnetic hysteresis allows materials to retain magnetic states, which is essential for storing binary data in devices like hard drives and magnetic tapes. - What are the applications of magnetic hysteresis in electrical engineering?
Magnetic hysteresis is used to design transformers and motors with low energy loss, as well as in magnetic sensors and shielding applications.